2024 Field Trial Shows Yield Differences Between Italian and Asian Cultivars
As part of Purdue University’s Field Production of Horticulture Crops class, Dr. Langenhoven established a comprehensive eggplant cultivar demonstration at the Meigs Horticulture Facility near Lafayette during the 2024 growing season. This hands-on educational project served a dual purpose: providing students practical crop management experience while generating valuable performance data on eight diverse eggplant cultivars under Indiana growing conditions. The results from this demonstration offer commercial vegetable growers throughout the state evidence-based insights to guide their cultivar selection decisions for maximum productivity and market appeal in the coming season.
Table 1: Eggplant cultivar characteristics.
| Cultivar | Seed Company | Days to Maturityz | Fruit Length (inches) |
| Asian Type | |||
| Ping Tung | Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds | 70 | 14 |
| Orient Express | Johnny’s Selected Seeds | 58 | 8-10 |
| Chinese String | Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds | 75 | 10-15 |
| Shikou | Harris Seeds | 75 | 6-8 |
| Italian Type | |||
| Nigral | Johnny’s Selected Seeds | 65 | 8-10 |
| Dancer | Johnny’s Selected Seeds | 65 | 7-8 |
| Annina | Johnny’s Selected Seeds | 65 | 6-8 |
| Rolandia | Territorial Seeds | 65 | 8 |
z Days to maturity from transplanting to mature fruit

Figure 1. Italian eggplant varieties included in demonstration planting (Photo by: Petrus Langenhoven).

Figure 2. Asian eggplant varieties included in demonstration planting (Photo by: Petrus Langenhoven).
Demonstration Setup and Management
The class evaluated four Italian-type and four Asian-type eggplant cultivars using the following production system:
Soil Conditions and Fertility
- Drummer soil series with 2.7% organic matter and pH 6.5
- Pre-plant soil test results: 24 ppm P, 111 ppm K, 190 ppm Mg, 1,800 ppm Ca
- Cation exchange capacity: 12.1 meq/100g
- Fertilization: 1000 lb/A of 9-23-30 and 150 lb/A of Urea (46-0-0), providing 159 lb N/A, 230 lb P₂O₅/A, and 300 lb K₂O/A applied during bed formation
Planting Schedule and Layout
- Seeding date: April 16, 2024
- 72 cell plug trays were placed on Redi-Heat HD heat mats at 80◦F to facilitate even and faster germination
- Transplant date: May 14, 2024
- Planting density: 1.5 ft between plants, 6.5 ft between beds (center-to-center), achieving 4,468 plants per acre
- Demonstration configuration: Two 180-foot rows with 30 plants per cultivar (non-replicated demonstration trial)
Crop Management
- Weed control: Pre-plant applications of Liberty (May 8) and Dual Magnum II (May 10)
- Plant support: Wooden stakes and string installed four weeks after transplanting
- Irrigation: Single drip tape per row (Rivulis T-tape 5/8″ with 12-inch emitter spacing, 0.22 GPM/100 ft flow rate)
- Pest management: No insecticide or fungicide applications were necessary due to low pest and disease pressure
- Harvest period: Weekly harvests from weeks 8-18 after transplanting, concluding on September 13
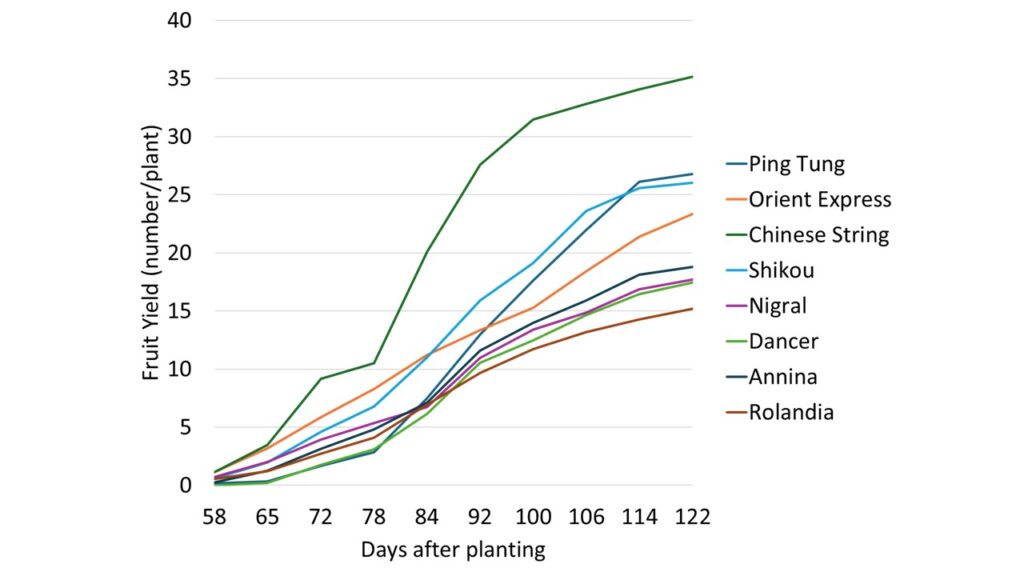
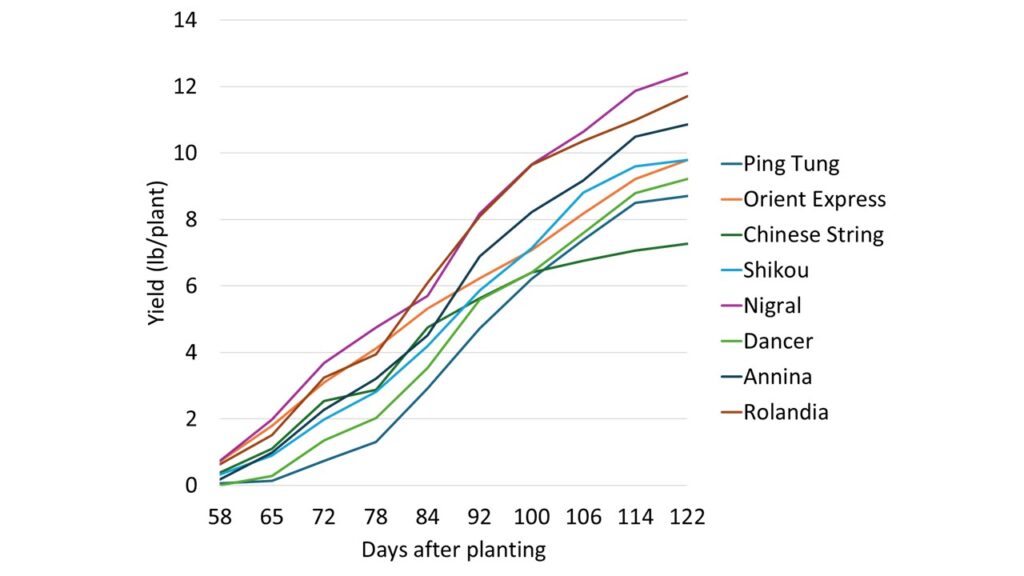
Key Findings by Cultivar Type
Italian-Type Eggplants: Higher Overall Yields
Italian-type cultivars consistently outperformed Asian types in terms of total marketable yield per acre:
Table 2. Marketable yield of Italian eggplant cultivars
| Cultivar | Fruit per plant | Yield (lb/plant) | Fruit Weight (oz) | Fruit per acre | Yield (lb/acre) |
| Nigral | 17.7 | 12.4 | 11.2 | 79,049 | 55,446 |
| Dancer | 17.5 | 9.2 | 8.4 | 78,041 | 41,161 |
| Annina | 18.8 | 10.9 | 9.2 | 83,917 | 48,495 |
| Rolandia | 15.2 | 11.7 | 12.3 | 67,914 | 52,320 |
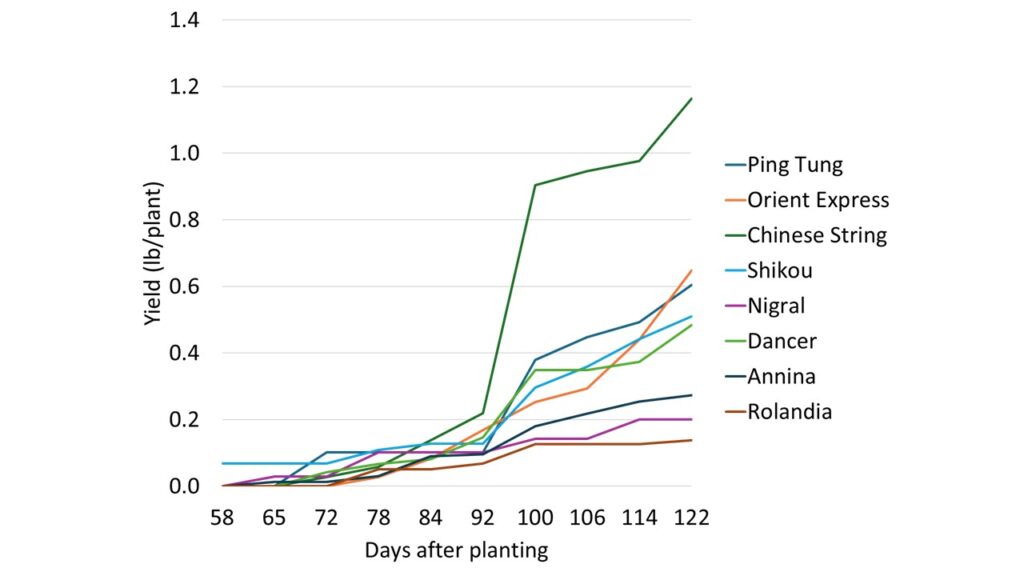
Table 3. Unmarketable yield of Italian eggplant cultivars
| Cultivar | Fruit per plant | Yield (lb/plant) | Yield (lb/acre) | Number of Fruit (%) |
| Nigral | 0.3 | 0.2 | 894 | 1.7 |
| Dancer | 1.3 | 0.5 | 2,160 | 6.8 |
| Annina | 0.6 | 0.3 | 1,222 | 2.9 |
| Rolandia | 0.3 | 0.1 | 618 | 1.7 |
Performance Highlights
- Nigral produced the highest overall yield (55,446 lb/A) with excellent fruit quality
- Rolandia grew the heaviest individual fruits (12.3 oz) with minimal unmarketable yield
- Annina produced well but also had the second highest unmarketable yield. Marketable yield losses were due to color fading, which might have been due to the fruit having passed its best harvest date (weekly harvest schedule)
- Dancer showed higher unmarketable yield (2,160 lb/A) primarily due to color fading from sun exposure
Asian-Type Eggplants: Specialized Production Options
Asian varieties offered different characteristics suitable for specialty markets:
Table 4. Marketable yield of Asian eggplant cultivars
| Cultivar | Fruit per plant | Yield (lb/plant) | Fruit Weight (oz) | Fruit per acre | Yield (lb/acre) |
| Ping Tung | 26.8 | 8.7 | 5.2 | 119,621 | 38,892 |
| Orient Express | 23.3 | 9.8 | 6.7 | 104,253 | 43,721 |
| Chinese String | 35.2 | 7.3 | 3.3 | 157,125 | 32,507 |
| Shikou | 26.0 | 9.8 | 6.0 | 116,354 | 43,706 |
Table 5. Unmarketable yield of Asian eggplant cultivars
| Cultivar | Fruit per plant | Yield (lb/plant) | Yield (lb/acre) | Number of Fruit (%) |
| Ping Tung | 1.7 | 0.6 | 2,701 | 6.1 |
| Orient Express | 1.9 | 0.6 | 2,895 | 7.6 |
| Chinese String | 8.0 | 1.2 | 5,203 | 18.5 |
| Shikou | 1.3 | 0.5 | 2,281 | 4.7 |
Performance Highlights
- Orient Express and Shikou both achieved top yields among Asian types (approximately 43,700 lb/A)
- Chinese String produced the highest number of fruits per plant (35) but with smaller individual fruit size (3.3 oz). It performed well early in the season, up to 92 days after transplanting, but showed reduced tolerance to extreme heat later
- Shikou demonstrated the lowest unmarketable yield and excellent quality, emerging as a favorite
- Ping Tung performed well. However, it only started to produce significant yields about 10 days later (at 78 days after transplanting) than the other cultivars
Production Timing Observations
All cultivars demonstrated excellent yield potential during the first five weeks of harvest (58 to 92 days after transplanting). Most cultivars maintained good quality throughout the season, with Rolandia, Nigral, and Annina showing particularly consistent marketable production even during later harvest weeks.
Recommendations for Indiana Growers
- For traditional markets seeking large fruits
- Nigral offers exceptional yield combined with good fruit size
- Rolandia provides premium-sized fruit with minimal cullage
- For specialty and ethnic markets
- Shikou and Orient Express provide excellent options for Asian-type eggplant production
- Chinese String is ideal for stir-fry applications but may require more careful management during heat waves
- Harvest timing considerations
- More frequent harvesting than our weekly schedule may reduce color fading issues observed in some cultivars, particularly Dancer
- Early-season production (July-early August) showed strongest performance across all varieties
Acknowledgements
This demonstration trial was supported by Chris Adair (Purdue Student Farm Manager), Purdue Student Farm Interns, and visiting scholar Sofia Catucuamba, and the staff of Meigs, Chloe Henscheid, and Wil Browm-Grimm for their support during the production phase of the experiment.
For more information about this trial or eggplant production recommendations for Indiana, contact your local Purdue Extension office or visit Midwest Vegetable Production Guide.